Species traits and foodweb complexity interactively affect a food web Biology Diagrams Such impacts are particularly pronounced in tropical regions where rapid transformation of rainforest to intensive agriculture (e.g., to oil palm or sugar cane plantations) is occurring. Yet, there is very little research-based evidence of how tropical stream food webs respond to increasing land-use intensification. Furthermore, recent studies

Beyond species extinctions, deforestation also disrupts the intricate food webs that connect different organisms within an ecosystem. The loss of keystone species, those that play a critical role in maintaining the ecosystem's structure and function, can have cascading effects, further destabilizing the environment.
Deforestation impacts on river food webs: comparing tropical and ... Biology Diagrams
5 ways to stop deforestation in our food Our 10 myths about deforestation 8 things to know about palm oil Bringing our world back to life. Join the race to save our world. Sign up to be kept informed about our conservation work and how you can help such as fundraising, campaigning and events.
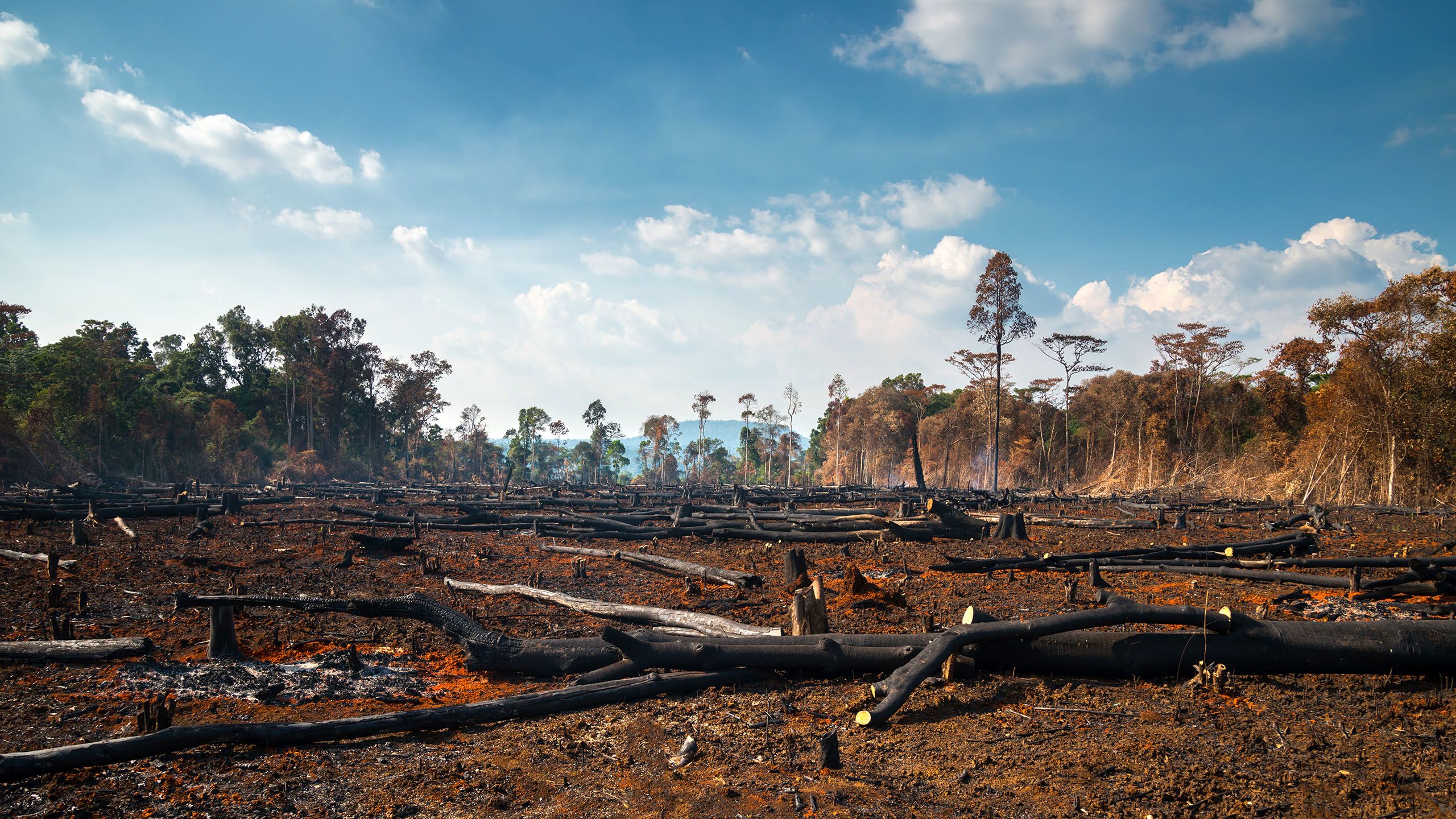

Human activities, including deforestation, urbanization, and pollution, have significant and often detrimental effects on forest food webs, disrupting the delicate balance of energy flow and trophic interactions. The removal of trees and vegetation not only reduces habitat availability for various species but also alters energy pathways within

Forests: Guardians Of Food Security And Climate Resilience Biology Diagrams
(a) An intact food web; (b) a food web subject to species loss due to extinction or overharvesting; (c) a food web affected by addition of non-native species at different trophic levels; (d) a food web exposed to bottom-up effects of eutrophication or pollution with potential biomagnification up the food chain; (e) a food web subject to the disruption of connectivity with the adjacent All five of the nodes are effects and causes of each other - that is, a loss of biodiversity causes food insecurity, which leads to more deforestation, which leads to greater CO2 emissions, and so on. For example, if current deforestation rates continue throughout the years, the Amazon's soy production could fall by 25% by 2050.
