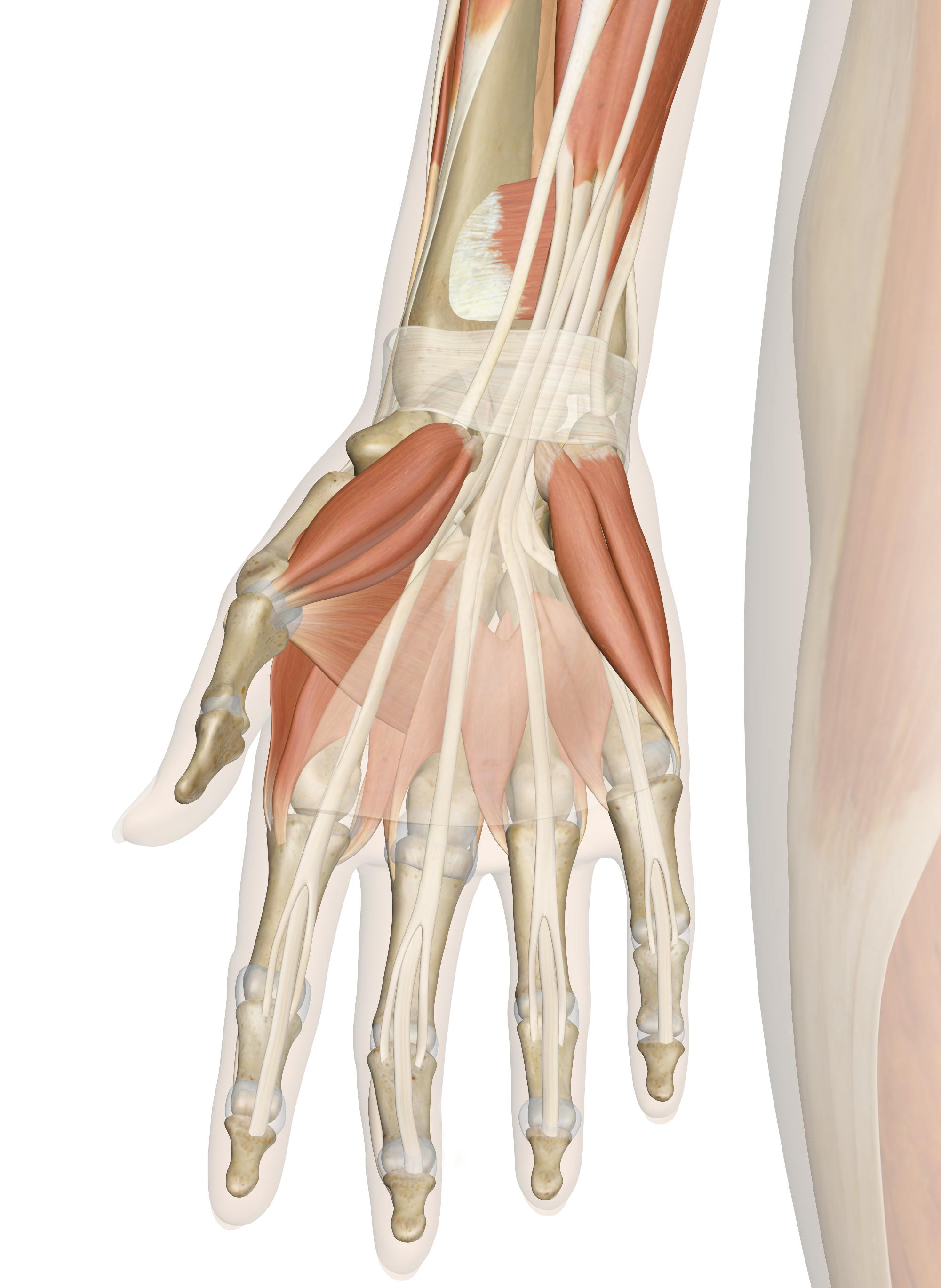
Human Hand Muscles Anatomy Medical Illustration3d Stock Illustration Biology Diagrams Learn about the bones, joints, ligaments, muscles, and nerves of the human hand, an extraordinary part of the upper limb. See detailed diagrams and descriptions of the hand's anatomy and how it works. The thenar muscles, which form the bulge of muscles evident at the base of the thumb, are essential to the hand's flexibility and gripping ability. One of these muscles, the opponens pollicis, moves the thumb across the hand to oppose the other fingers, allowing us to pinch a small object between the thumb and finger to pick it up.

Learn about the structure and function of the hand, the most distal part of the upper limb. Explore the carpal, metacarpal and phalangeal bones, the thenar, hypothenar and lumbrical muscles, and the median, ulnar and radial nerves and arteries. Learn about the 11 intrinsic and 15 extrinsic muscles in each hand that help with thumb, finger, and palm movements. See the muscle origin, insertion, action, and innervation for each muscle group.

The Muscles of the Hand: Anatomy and 3D Illustrations Biology Diagrams
The Hand Anatomy is complex and important to understand, it consists of 27 bones, 27 joints, 34 muscles and a lot of ligaments that connects joints together. To understand the complex hand anatomy, we will divide this article into: bones anatomy, joints anatomy, muscles and ligaments anatomy. Bony Hand Anatomy Metacarpals Bones Learn about the anatomy and function of the muscles of the hand, which are divided into extrinsic and intrinsic groups. The extrinsic muscles are located on the forearm and the intrinsic muscles are located within the hand itself.

Learn about the hand muscles, their attachment, nerve supply and action. The hand muscles are divided into extrinsic and intrinsic groups, and include thenar, hypothenar, lumbrical and interossei muscles. Learn about the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the hand, their attachments, actions and innervation. See 3D models, dissection images and diagrams of the thenar, hypothenar, lumbricals and interossei muscles.